What are Silicon Carbide (SiC) ceramics?
Since the late 19th century, this compound of silicon and carbon, known as silicon carbide ceramics (SiC), has evolved from an abrasive powder to a cornerstone material for high-performance engineering. Today, SiC ceramics are indispensable in industries ranging from semiconductors and electronics to aerospace, automotive, energy and chemical processing.
What is silicon carbide? Scientifically, it is a covalently bonded silicon carbide compound with the chemical formula SiC that exhibits a unique crystal structure and can exist in different polytypes (3C, 4H, 6H). Its high hardness (Mohs 9.5), low density (~3.1 g/cm³), high melting temperature (~2,700 °C) and excellent thermal conductivity of silicon carbide make it ideal for demanding applications where metals or plastics fail.
At Zihao Ceramics, we offer engineered silicon carbide parts that are customized to provide unmatched precision, consistency and reliability.
jump to
Advantages of Silicon Carbide Ceramics
The unique combination of mechanical, thermal and electrical properties makes SiC stand out among technical ceramics.
Industry Applications
The use of silicon carbide spans a wide range of industries due to its superior performance:





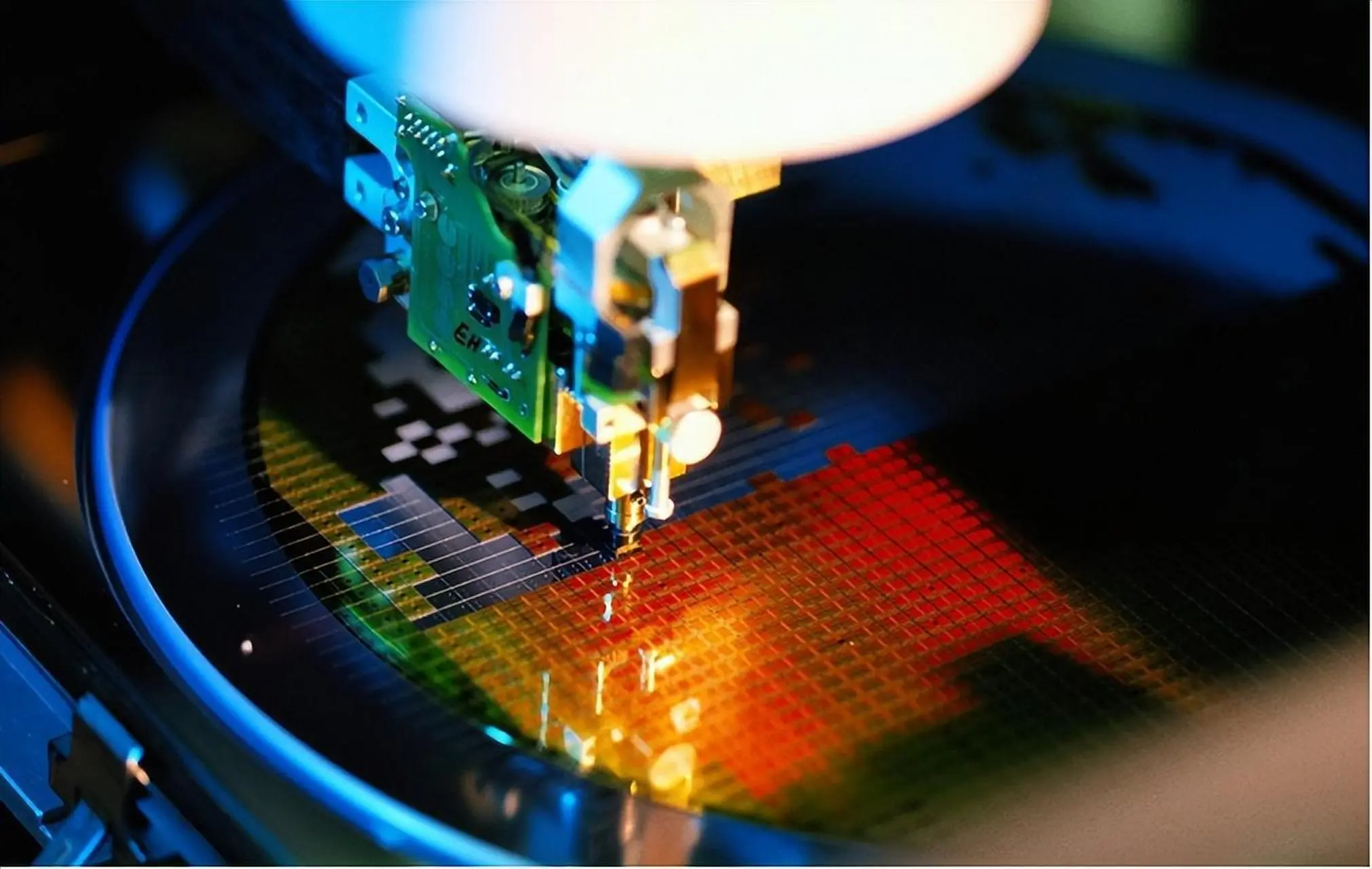

Types of Silicon Carbide Ceramics
At Zihao, we offer a wide range of high-performance silicon carbide materials optimized for the application to meet different engineering requirements:
Pressureless Sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramics (SSIC)
Pressureless Sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramics (SSiC) are high performance structural ceramics produced by a high temperature, pressureless sintering process. Their main component is high-purity silicon carbide powder. The sintering process does not require metal binders or external pressure, resulting in extremely high purity and density and thus excellent overall properties. This material is widely used in extremely harsh environments due to its excellent mechanical strength, wear and corrosion resistance.
Main features
typical application
Production process
Pressureless sintered silicon carbide ceramics are made from high-purity SiC powder, which is then formed into molds with a small amount of sintering aid and pressureless sintered at temperatures in excess of 2,000°C. The sintered silicon carbide ceramics are then sintered into molds with a small amount of sintering aid. This process gives the material a dense structure close to the theoretical density with fine, uniform grains, thus ensuring excellent overall performance.
Reaction Sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramics (SISiC)
Reaction Sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramics (SISiC) is a high performance ceramic material made from silicon carbide (SiC) powder and a carbon source. Liquid silicon is infiltrated into green objects at high temperatures, creating a reaction that produces new silicon carbide. Compared to pressureless sintered silicon carbide (SSiC), SISiC offers lower production temperatures and a more flexible process, enabling the fabrication of large and complex shaped structural components. As a result, it enjoys a wide range of industrial applications.
Main features
typical application
Production process
The process of preparing reactive sintered silicon carbide typically involves:
Advantages of this method include process simplicity, low sintering temperatures, minimal dimensional shrinkage, and the ability to produce large, complex parts close to net size. However, the high temperature strength and oxidation resistance are slightly inferior to SSiC due to the presence of residual silicon.
Main Properties of Silicon Carbide
| performances | unit (of measure) | unpressurized silicon carbide | Reactive silicon carbide | silicon nitride |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| color | -- | dark gray | dark gray | dark gray |
| intensity | g/cm³ | 3.15 | 3.02 | 3.2 |
| porosity | % | ≤0.1 | ≤0.1 | -- |
| durometer | GPa | 22 | 22 | 15 |
| compressive strength | MPa | 2600 | 2600 | 2500 |
| bending strength | MPa | 400 | 250 | 700 |
| modulus of elasticity | GPa | 410 | 330 | 300 |
| Maximum operating temperature | ℃ | 1400 | 1000 | 1100 |
| heat conductivity | W/(m・K) | 100~120 | 45 (1200°C) | 15~20 |
| coefficient of thermal expansion | 1 x 10-6/°C | 4 | 4.5 | 3 |
*The above values are typical material properties and may vary depending on product configuration and manufacturing process. For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Chemical Properties of Silicon Carbide Materials
When the temperature in the oxygen reaction reaches 1300°C, a protective layer of silicon dioxide forms on the surface of the silicon carbide crystals. With the thickening of the protective layer, the internal silicon carbide is resisted and continues to combine, so that the silicon carbide crystal silicon carbide has good chemical resistance. In terms of corrosion resistance, SiC materials have strong acid resistance due to the role of the protective film of silica, but poor alkali resistance.
Silicon Carbide Ceramics Application Examples
Silicon Carbide (SiC) ceramics from Good Ceramics combine outstanding hardness, excellent thermal conductivity, superior wear resistance, and superior chemical stability, making them one of the most advanced ceramic materials for demanding industrial applications. With high melting points, low thermal expansion, and the ability to withstand extreme environments, SiC ceramics are ideal for industries that require durability, efficiency, and long service life.
Major applications of silicon carbide ceramics:
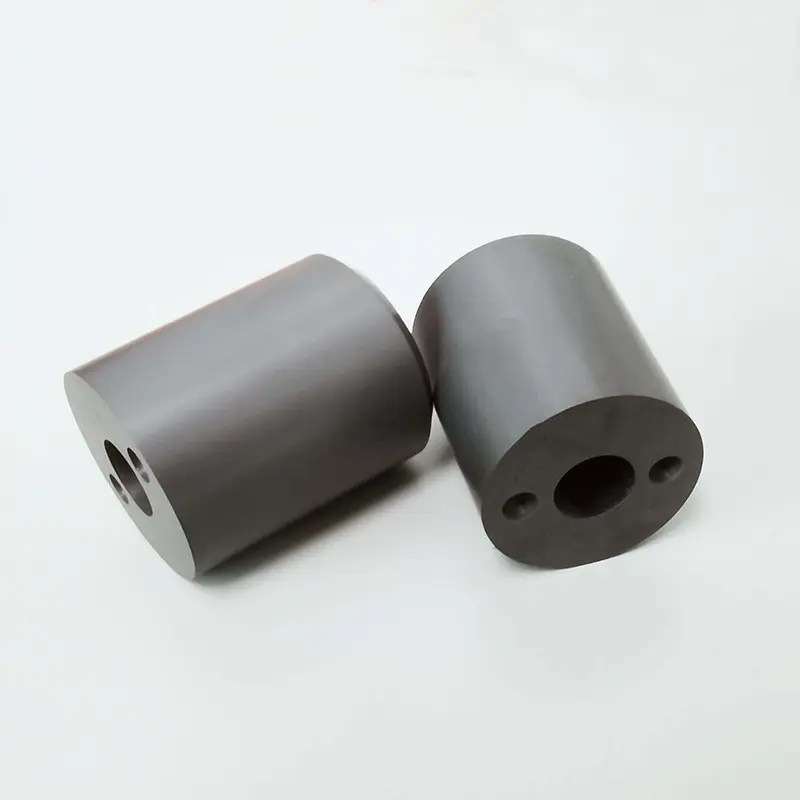
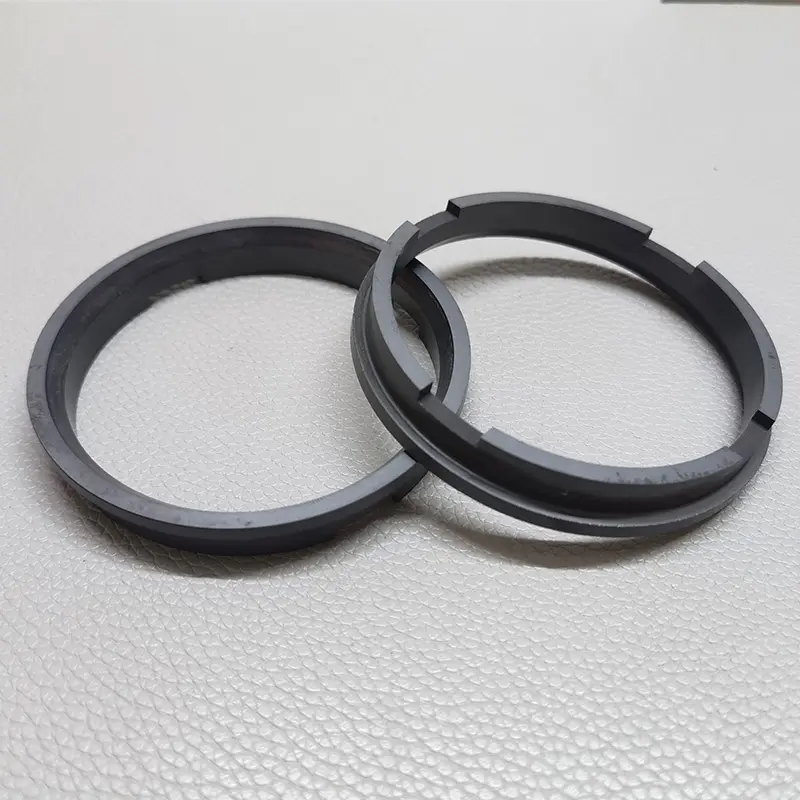
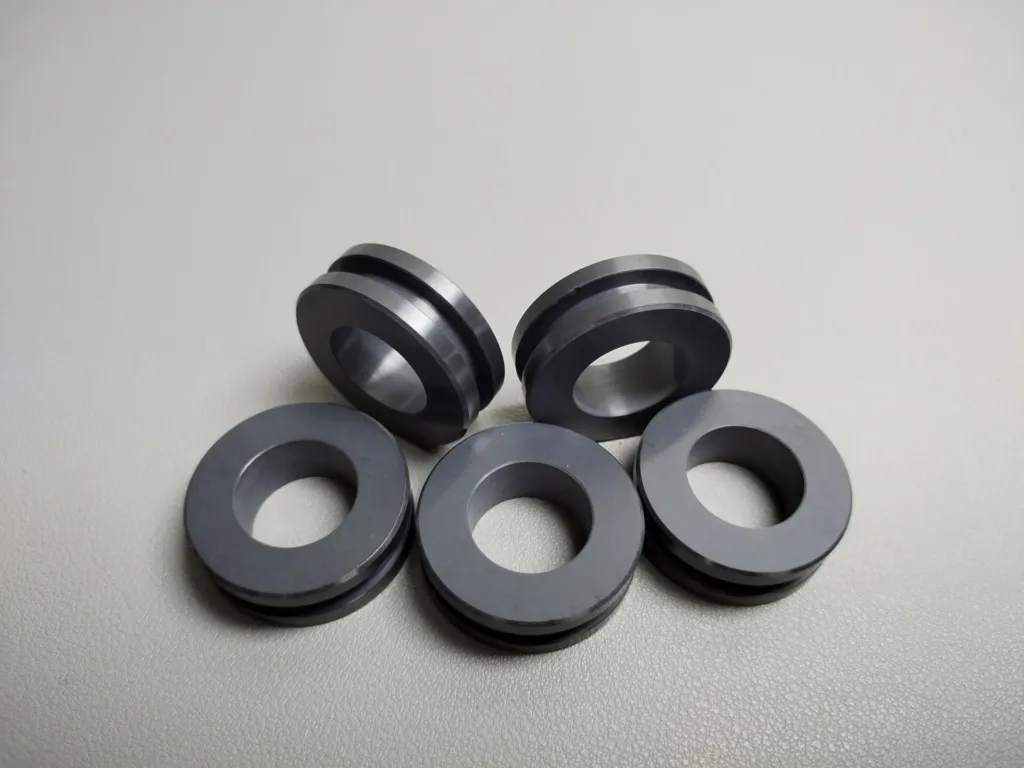
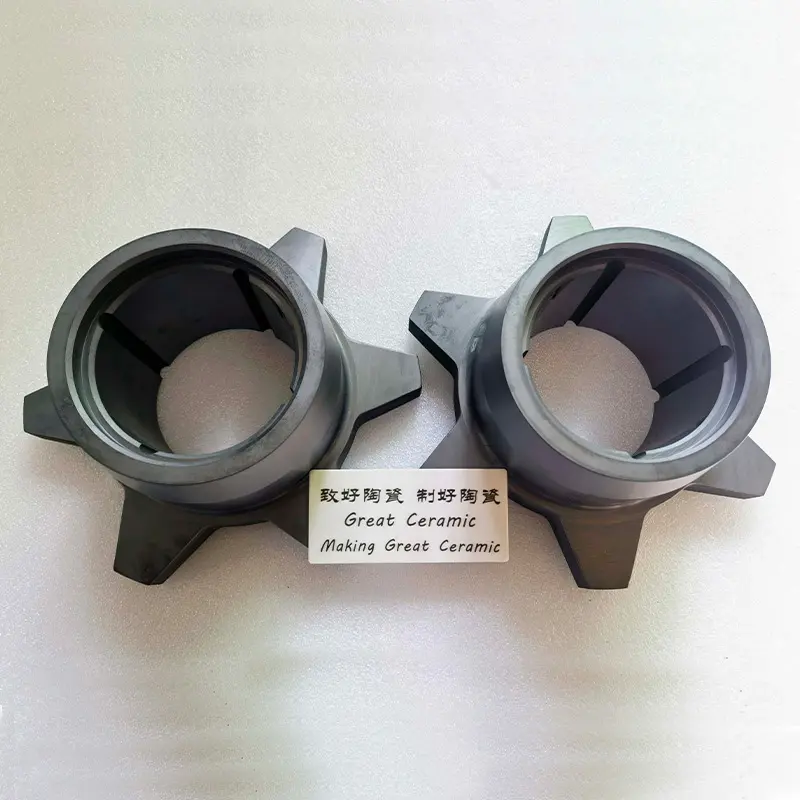








Silicon Carbide Ceramics Processing
Silicon Carbide (SiC) ceramics are known for their extremely high hardness, high thermal conductivity and excellent wear resistance, making them one of the most challenging technical ceramics to machine. At Good Ceramics, we offer a full range of SiC machining services that provide industry-leading precision, performance, and reliability.
During the machining process, we utilize advanced diamond grinding, precision lapping and fine polishing techniques to achieve micron tolerances and superior surface finishes. These capabilities enable us to meet the stringent structural accuracy and surface quality requirements of mechanical seals, semiconductor substrates, crucibles, heat exchangers and aerospace components.
With years of technical expertise and state-of-the-art equipment, Grand Ceramics not only offers standardized silicon carbide parts, but also develops customized and complex components for specific industrial needs, ensuring high reliability and long service life under extreme operating conditions.
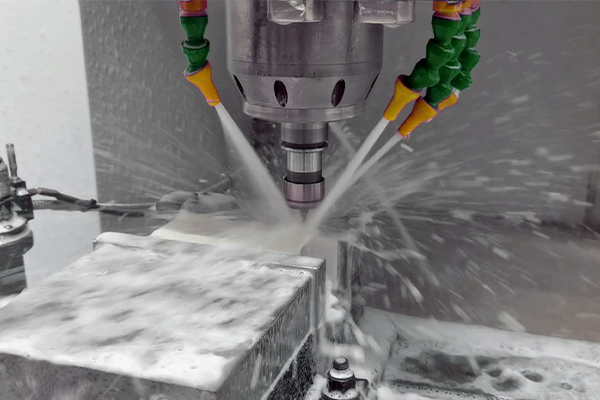

CNC grinding and milling
CNC milling, turning and grinding to micron tolerances.
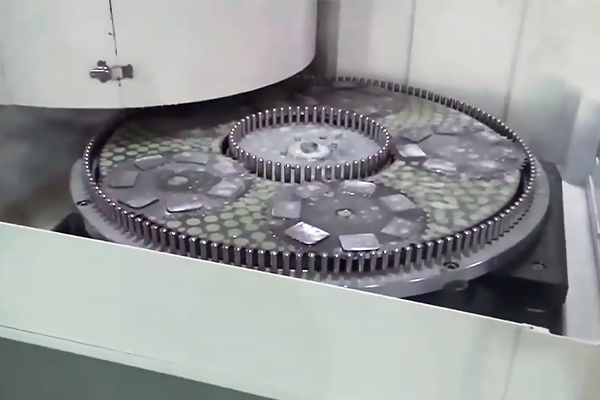

Grinding and polishing
Surface polishing results in smooth surfaces and optical grade surfaces.
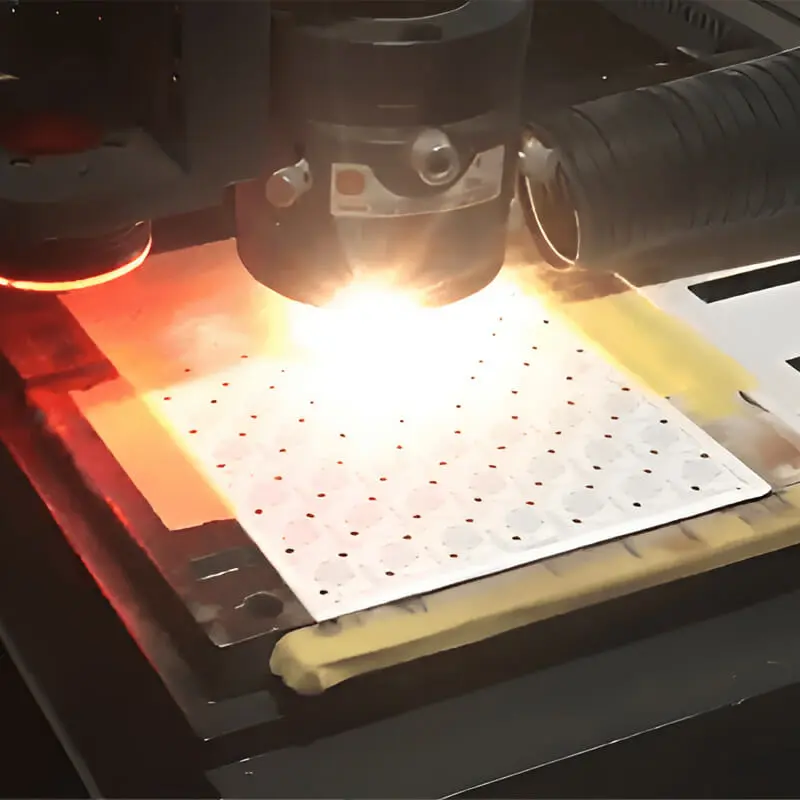
Ceramic Laser Cutting
For laser drilling and cutting of complex geometries.
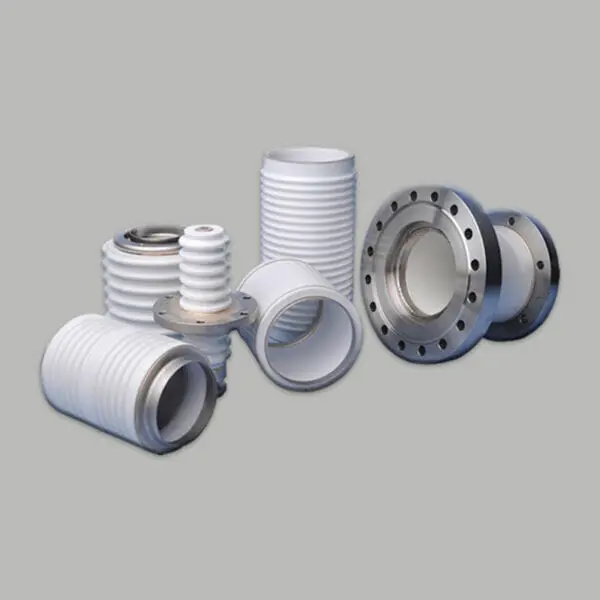

Metallization and welding
Metallization (Mo/Mn, W) for ceramic-to-metal brazing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Related Products
Advanced Ceramics Manufacturing Specialist






