What are beryllium oxide (BeO) ceramics?
Beryllium oxide, commonly referred to as BeO, is a highly specialized ceramic material known for its excellent thermal conductivity, high electrical resistivity, and outstanding mechanical strength. Beryllium oxide has the chemical formula BeO, which is also often denoted as beryllium oxide chemical formula, beryllium oxide chemical formula, or beryllium oxide chemical formula. As a high-performance ceramic, BeO stands out among advanced materials for its unique electrical insulation and thermal conductivity comparable to metals such as aluminum. This dual property makes beryllium oxide an irreplaceable material for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and electrical isolation.
jump to
Advantages of beryllium oxide
BeO beryllium oxide ceramics have a range of properties that make them highly sought after in advanced technologies.
Industry Applications
Beryllium oxide ceramics, because of its extremely high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation properties, is widely used in high-power electronics and radio frequency devices, heat dissipation substrates, semiconductor packaging and microwave devices, electrical insulation structure, as well as lasers, vacuum tubes and nuclear energy technology in the high-temperature insulators and heat-resistant components, but also used to manufacture high-purity crucibles, thermal conductive components and special sensors, in the need for efficient heat dissipation and insulation of the key occasions They play an irreplaceable role in critical applications where efficient heat dissipation and insulation are required.






Available grades of beryllium oxide materials
Goodwill Ceramics offers a wide range of beryllium oxide product grades and specifications to meet application needs:
B-97 grade beryllium oxide ceramics
B-97 grade beryllium oxide ceramics are high-performance technical ceramics composed primarily of high-purity BeO (typically about 97%). It combines high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation with excellent mechanical strength and high temperature stability. As such, it plays a vital role in high-end applications such as electronics, microwave and nuclear energy.
Main Performance Characteristics
typical application
hedge
BeO dust is harmful to human beings, and dust emission must be strictly controlled during processing and safety protection measures must be implemented.
Finished ceramics are safe and stable under normal operating conditions.
B-99 grade beryllium oxide ceramics
B-99 grade beryllium oxide ceramic is a high purity (BeO content ≥99%) advanced ceramic material. Compared with B-97 grade, it has higher chemical purity and excellent physical properties, and is especially suitable for applications requiring extremely high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. Its performance is at the high end of beryllium oxide ceramics.
Main Performance Characteristics
typical application
hedge
As with B-97, strict precautions must be taken during processing to avoid inhalation of BeO dust.
Finished ceramics are stable and safe during packaging, assembly and use.
B-99.5 grade beryllium oxide ceramics
B-99.5 grade beryllium oxide ceramic is an ultra-high purity (BeO ≥ 99.5%) specialty ceramic material, one of the highest purity beryllium oxide ceramic grades. Compared to B-97 and B-99, it has excellent thermal conductivity, electrical properties and chemical stability, making it particularly suitable for advanced technologies with stringent requirements for thermal management and electrical performance.
Main Performance Characteristics
typical application
summarize
B-99.5 grade beryllium oxide ceramics represent the highest grade of beryllium oxide ceramics, combining extremely high thermal conductivity, excellent electrical insulation, and superior high-temperature and radiation stability.B-99.5 grade beryllium oxide ceramics are mainly used in aerospace and nuclear energy, high-power electronic devices, and cutting-edge scientific research, and are one of the highest-performance insulating and thermal conductive ceramics.
Beryllium oxide attenuation ceramics
Beryllium oxide attenuating ceramic is a functional ceramic developed on the basis of high purity BeO. Through doping and special processes, its electromagnetic properties are altered to provide electromagnetic wave attenuation (absorption and dissipation) capabilities while maintaining BeO's excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. These ceramics integrate thermal management and electromagnetic energy control, and are key materials for microwave, RF and high-power electronic applications.
Key attributes
typical application
summarize
Beryllium oxide attenuating ceramics combine high thermal conductivity, strong insulation, and electromagnetic attenuation properties, making them an integral part of microwave devices, RF power electronics, EMC systems, and aerospace/defense applications.
Main properties of beryllium oxide
The following values are typical material properties and may vary depending on product configuration and manufacturing process. Please feel free to contact us for further details.
| properties | B-97 | B-99 | B-99.5 |
| Dielectric constant (1MHz) | 6.9±0.4 | 6.6±0.2 | 6.6±0.2 |
| Dielectric constant (~10 GHz) | 6.9±0.4 | 6.9±0.2 | 6.8±0.2 |
| Dielectric loss tanδ (1MHz) | ≤4×10-⁴ | ≤4×10-⁴ | ≤4×10-⁴ |
| Dielectric loss tanδ (10 GHz) | ≤8×10-⁴ | ≤6×10-⁴ | ≤4×10-⁴ |
| Volume resistivity (25°C) | ≥ 1×10¹⁴ | ≥ 1×10¹⁴ | ≥ 1×10¹⁴ |
| DC Breakdown Strength | ≥15 kV/mm | ≥30 kV/mm | ≥40 kV/mm |
| bending strength | ≥170 MPa | ≥ 200 MPa | ≥ 200 MPa |
| packing density | ≥ 2.85 g/cm3 | ≥ 2.85 g/cm3 | ≥ 2.88 g/cm3 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (25-500 degrees Celsius) | 7.0-8.5 × 10-⁶ | 7.0-8.0 × 10-⁶ | 7.0-8.0 × 10-⁶ |
| Thermal conductivity (25°C) | ≥ 200 W/m-Kelvin | ≥260 W/m-Kelvin | ≥ 285 w/m Kelvin |
| Thermal conductivity (100°C) | ≥160 W/m-Kelvin | ≥190 W/m -- Kelvin | ≥ 200 W/m-Kelvin |
| thermal shock resistance | uncracked | go through | go through |
| Chemically stable in 1:9 HCl | ≤ 0.3 mg/cm2 | ≤ 0.1 mg/cm2 | ≤ 0.1 mg/cm2 |
| Chemical stability in 10% NaOH | ≤ 0.2 mg/cm2 | ≤ 0.1 mg/cm2 | ≤ 0.1 mg/cm2 |
| leak rate | ≤1 x 10-¹⁰ Pa-m3/s | ≤5 x 10-¹² Pa-m3/s | ≤5 x 10-¹² Pa-m3/s |
| Average particle size | 12-30 microns | 10-20 microns | 10-20 microns |
Key Performance Comparisons - BeO vs. other technical ceramics
| properties | Beryllium oxide (BeO) | Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃ 99%) | Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | Shapal (AlN-SiC) |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m-K) | 230 - 260 | 20 - 30 | 170 - 180 | 85 - 90 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (x10-⁶/K) | 7.0 - 8.5 | 6.5 - 8.0 | 4.5 - 5.5 | 4.5 - 5.5 |
| Dielectric Constant (1MHz) | 6.7 | 9.8 | 8.6 - 9.0 | 7.0 - 7.5 |
| Dielectric loss (tanδx10-⁴) | 1 - 5 | 1 - 2 | 1 - 10 | 5 - 15 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 170 - 300 | 300 - 400 | 300 - 400 | 450 - 600 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.85 - 3.01 | 3.85 - 3.95 | 3.25 - 3.35 | 3.10 - 3.20 |
Beryllium oxide application cases
ToHo Ceramics' beryllium oxide (BeO) ceramics combine ultra-high thermal conductivity, excellent electrical insulation, low dielectric constants, and superior high-temperature stability, making them one of the most advanced ceramic solutions for demanding industries.BeO ceramics have a coefficient of thermal expansion close to that of silicon, which makes them ideal for high-performance electronic packaging and thermal management.
The main applications of BeO ceramics:


Toxicity of beryllium oxide ceramics
While high purity beryllium oxide ceramics are very safe, it should not be overlooked that beryllium oxide dust is toxic to humans. This is just as plastics do not produce toxins when used, but materials made from plastics are generally toxic for the same reason. Beryllium oxide ceramics processed into solid form do not pose a particular health hazard.
Beryllium oxide processing
Beryllium oxide ceramics have very high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation, making them ideal for power electronics and high frequency devices. ZhiHao Ceramics has a full range of beryllium oxide ceramics machining capabilities to provide customers with industry-leading performance, durability, and precision.
During processing, we utilize diamond grinding and precision polishing technologies to achieve micron-level accuracy, meeting the stringent structural accuracy and surface quality requirements of high-power modules, microwave devices, and laser systems. We also support metallization, brazing and encapsulation processes, enabling customers to apply beryllium oxide ceramics to a wider range of industry sectors.
With many years of technical experience and advanced equipment, we not only provide standardized parts, but also can customize complex structural components and high reliability products for our customers.
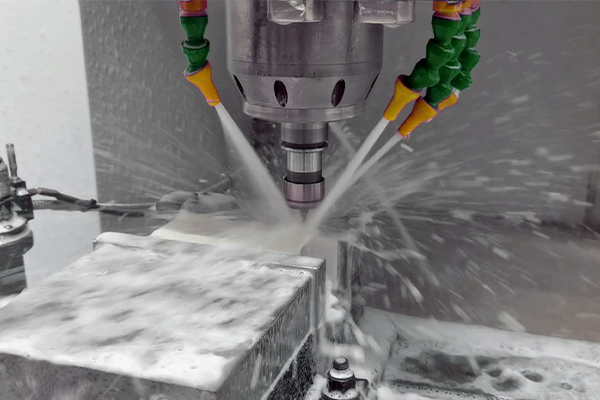

CNC grinding and milling
CNC milling, turning and grinding to micron tolerances.
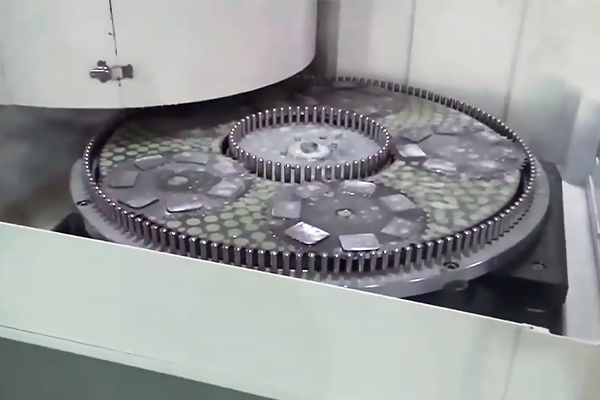

Grinding and polishing
Surface polishing results in smooth surfaces and optical grade surfaces.
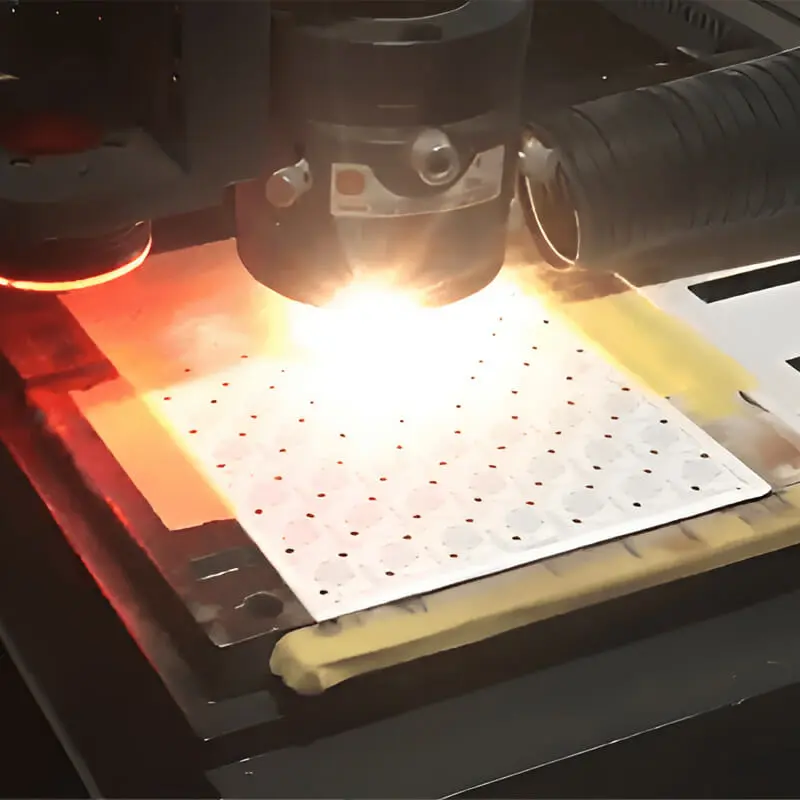
Ceramic Laser Cutting
For laser drilling and cutting of complex geometries.
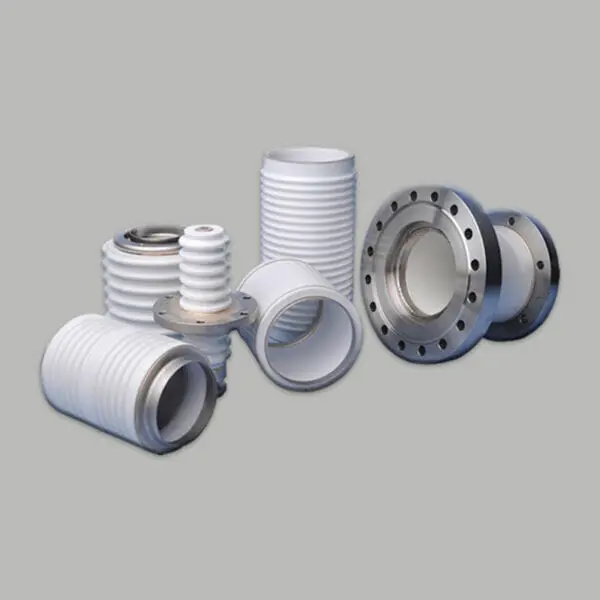

Metallization and welding
Metallization (Mo/Mn, W) for ceramic-to-metal brazing.
FAQ
Related Products

aluminum nitride
silicon nitride
Advanced Ceramics Manufacturing Specialist








